Kg Cm To N M
thedopedimension
Sep 15, 2025 · 5 min read
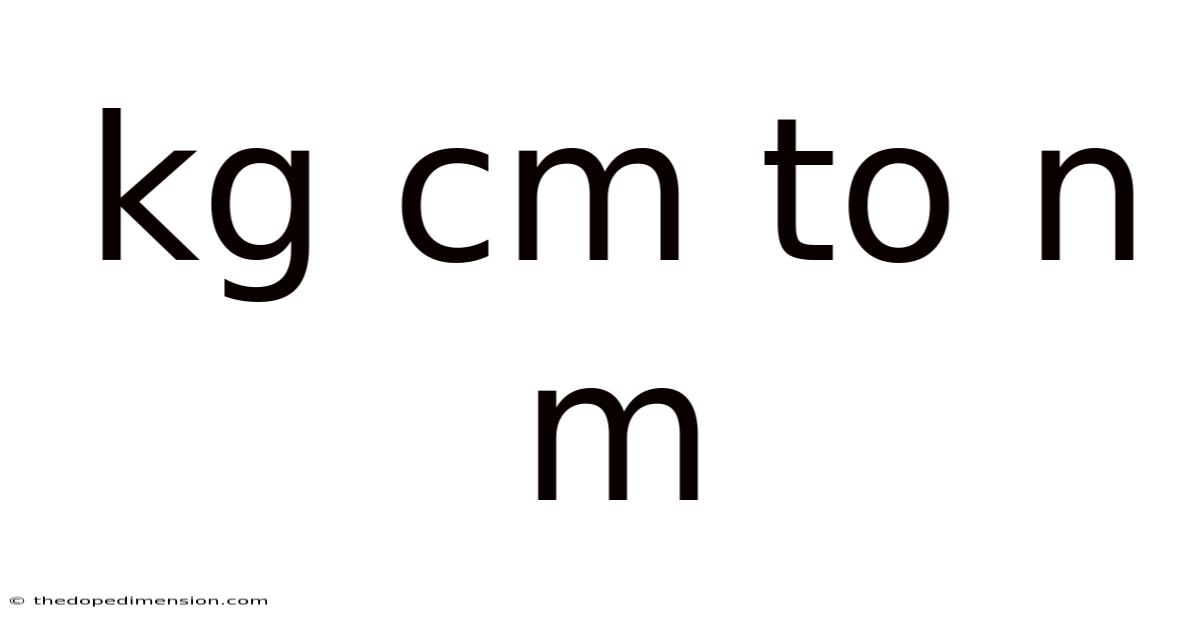
Table of Contents
Converting kg·cm to N·m: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the conversion between kilogram-centimeters (kg·cm) and Newton-meters (N·m) is crucial in various fields, particularly in mechanics, engineering, and physics. This seemingly simple conversion involves a deeper understanding of units and the principles of torque and force. This article provides a comprehensive guide to converting kg·cm to N·m, explaining the underlying principles, offering step-by-step instructions, addressing common misconceptions, and exploring real-world applications. Mastering this conversion will enhance your understanding of rotational mechanics and improve your problem-solving skills in relevant fields.
Introduction: Understanding Torque and Units
Torque, often represented by the symbol τ (tau), is the rotational equivalent of linear force. It's a measure of how much a force acting on an object causes that object to rotate. The SI unit for torque is the Newton-meter (N·m), representing the force (in Newtons) applied at a specific distance (in meters) from the axis of rotation. However, in certain contexts, particularly older engineering documentation or specific industries, you might encounter torque expressed in kilogram-centimeters (kg·cm). This unit reflects a mass (in kilograms) acting at a distance (in centimeters) from the pivot point. The key to converting between these units lies in understanding the relationship between mass, force, and acceleration.
The Fundamental Relationship: Force, Mass, and Acceleration
The conversion hinges on Newton's second law of motion: F = ma, where:
- F represents force (in Newtons)
- m represents mass (in kilograms)
- a represents acceleration (in meters per second squared, m/s²)
In the context of Earth's gravity, the acceleration due to gravity (g) is approximately 9.81 m/s². This means that a mass (m) experiences a force (F) equal to F = mg. This force is the weight of the object. This is crucial because the kg·cm unit implicitly incorporates this gravitational force.
Step-by-Step Conversion: kg·cm to N·m
Here's a step-by-step guide to converting torque from kg·cm to N·m:
-
Understand the Implicit Force: The kilogram in kg·cm represents a mass experiencing the Earth's gravitational pull. Therefore, we first need to calculate the force acting on this mass. Use the equation F = mg, where 'm' is the mass in kilograms and 'g' is the acceleration due to gravity (approximately 9.81 m/s²).
-
Convert Centimeters to Meters: The centimeter in kg·cm needs to be converted to meters to be consistent with the N·m unit. Since there are 100 centimeters in a meter, divide the centimeter value by 100.
-
Calculate the Torque in N·m: Now, multiply the force (F) calculated in step 1 by the distance (in meters) calculated in step 2. This product represents the torque in N·m.
Formula Summary:
The complete conversion formula can be summarized as:
Torque (N·m) = m (kg) * g (m/s²) * d (cm) / 100
Where:
- m = mass in kilograms
- g = acceleration due to gravity (approximately 9.81 m/s²)
- d = distance in centimeters
Example Calculation
Let's say we have a torque value of 50 kg·cm. Here's how to convert it to N·m:
-
Calculate the Force: F = m * g = 50 kg * 9.81 m/s² = 490.5 N
-
Convert Centimeters to Meters: d (meters) = 1 cm / 100 = 0.01 meters
-
Calculate the Torque: Torque (N·m) = 490.5 N * 0.01 m = 4.905 N·m
Therefore, 50 kg·cm is approximately equal to 4.905 N·m.
Common Misconceptions and Clarifications
-
Ignoring Gravity: A common mistake is to directly convert kg·cm to N·m without considering the gravitational force. This leads to inaccurate results. Remember, the kilogram in kg·cm implies weight, not just mass.
-
Units Consistency: Ensure all units are consistent throughout the calculation. Mixing centimeters and meters will result in errors. Always convert everything to the SI base units (kilograms, meters, seconds) before performing the calculation.
-
Static vs. Dynamic Torque: The conversion applies primarily to static torque, where the system is in equilibrium. In dynamic situations, other factors may need to be considered, depending on the specific problem.
Real-World Applications
The conversion between kg·cm and N·m is crucial in various applications, including:
-
Mechanical Engineering: Designing engines, gears, and other mechanical systems requires accurate torque calculations for optimal performance and safety.
-
Robotics: Controlling robotic arms and manipulators precisely relies on converting torque measurements to ensure smooth and controlled movements.
-
Automotive Engineering: Determining the torque output of an engine, as well as the torque capacity of various components, is essential for design, testing, and performance analysis.
-
Aerospace Engineering: In aircraft and spacecraft design, precise torque calculations are critical for structural integrity and maneuverability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: Why is the kg·cm unit still used if N·m is the standard SI unit?
- A: The kg·cm unit persists due to historical reasons and its prevalence in certain industries and older documentation. However, it’s always best practice to convert to N·m for consistency and easier comparison with other data.
-
Q: What if the torque is not expressed as a simple number, but as a function or an equation?
- A: In such cases, you'll need to apply the conversion formula (as shown above) to each component of the function or equation, ensuring consistency of units throughout.
-
Q: Does the value of 'g' (acceleration due to gravity) change the conversion significantly?
- A: The value of 'g' varies slightly depending on location. However, the difference is usually negligible for most practical applications. Using the standard value of 9.81 m/s² is sufficient for most engineering calculations.
-
Q: Can I convert N·m to kg·cm using the reverse of this process?
- A: Absolutely. You can reverse the process by dividing the torque in N·m by 'g' (9.81 m/s²) and then multiplying by 100 to get the distance in centimeters.
Conclusion
Converting kg·cm to N·m requires a clear understanding of the underlying physics principles, specifically the relationship between mass, force, acceleration, and torque. By following the step-by-step process outlined in this guide and understanding the common misconceptions, you can confidently perform this conversion and apply it to various practical problems in mechanics and engineering. Remember to always prioritize units consistency for accurate and reliable results. This knowledge is crucial for professionals in various fields and contributes to a deeper understanding of rotational mechanics and force systems. Through accurate conversions and a solid understanding of the fundamental principles, you can enhance your problem-solving capabilities and build more reliable and efficient systems.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Conversion Table Ounces To Quarts
Sep 15, 2025
-
220 Square Meters To Feet
Sep 15, 2025
-
Pm 3 To Cm 3
Sep 15, 2025
-
Whats 185 Cm In Feet
Sep 15, 2025
-
Short To Metric Ton Conversion
Sep 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Kg Cm To N M . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.