200 000 Kb To Mb
thedopedimension
Sep 04, 2025 · 5 min read
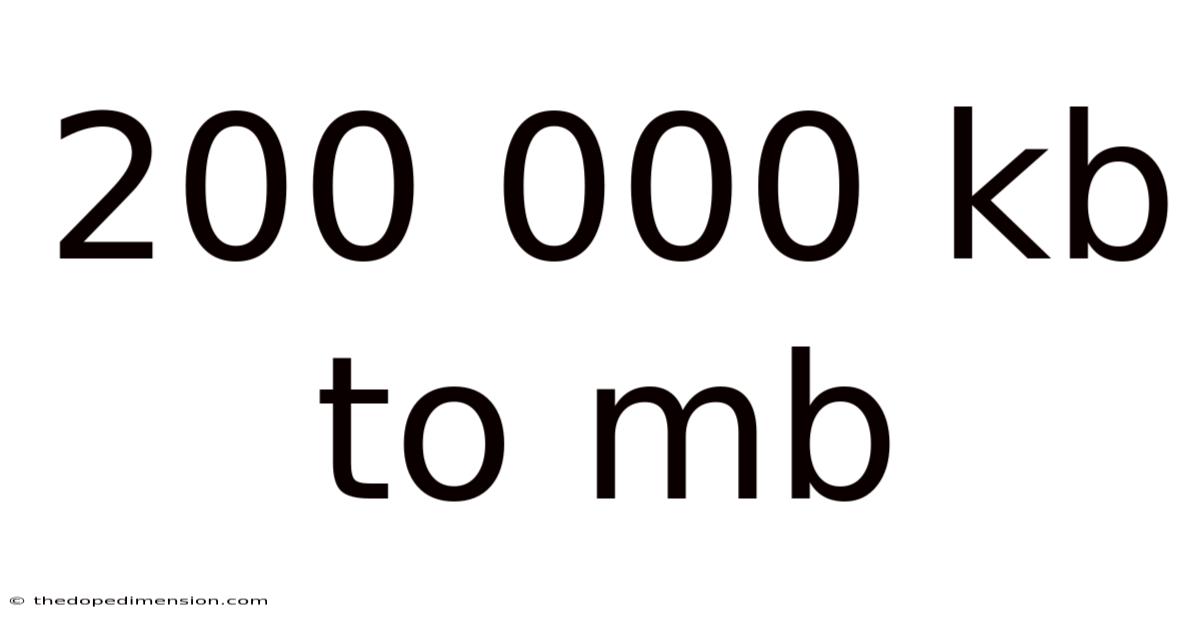
Table of Contents
Converting 200,000 KB to MB: A Deep Dive into Data Measurement
Understanding data storage and transfer requires familiarity with different units of measurement. One common conversion is from kilobytes (KB) to megabytes (MB). This article will comprehensively explain how to convert 200,000 KB to MB, explore the underlying principles of data measurement, and address common questions and misconceptions. We'll go beyond a simple calculation, delving into the practical implications of these conversions in everyday computing and data management.
Understanding Kilobytes (KB) and Megabytes (MB)
Before diving into the conversion, let's establish a clear understanding of kilobytes and megabytes. These are units used to measure digital information, representing the amount of data that can be stored or transferred.
-
Kilobyte (KB): A kilobyte is a unit of digital information equal to 1024 bytes. It's often simplified to 1000 bytes for ease of calculation, although the actual value is 2<sup>10</sup> bytes. This slight discrepancy arises from the binary nature of computing (based on powers of 2).
-
Megabyte (MB): A megabyte is a larger unit of digital information equal to 1024 kilobytes. Similarly, it's sometimes approximated to 1000 KB, but the precise value is 2<sup>20</sup> bytes.
Converting 200,000 KB to MB: The Calculation
The core conversion is straightforward: We divide the number of kilobytes by the number of kilobytes in a megabyte. Using the precise value of 1024 KB/MB:
200,000 KB / 1024 KB/MB = 195.3125 MB
Therefore, 200,000 KB is equal to 195.3125 MB.
If we use the simplified approximation of 1000 KB/MB:
200,000 KB / 1000 KB/MB = 200 MB
This approximation provides a quicker, less precise result. The difference highlights the importance of using the accurate conversion factor (1024) for precise calculations, especially when dealing with larger datasets where the small discrepancies accumulate.
The Significance of Precise Conversions
The difference between using 1000 and 1024 in the conversion might seem minor for smaller figures. However, this discrepancy becomes significant when dealing with larger files or datasets. In data storage and network management, accuracy is paramount. Using the approximate value consistently can lead to errors in capacity planning, data transfer estimations, and overall system performance. For example, a hard drive advertised as having 1 TB (terabyte) capacity might actually have slightly less usable space due to this binary-decimal difference.
Beyond KB and MB: A Look at Other Units
The hierarchy of data units extends beyond kilobytes and megabytes. Understanding the relationships between these units is crucial for comprehending data sizes and transfer speeds. Here's a common progression:
-
Byte (B): The fundamental unit of digital information, representing a single character or a small piece of data.
-
Kilobyte (KB): 1024 bytes
-
Megabyte (MB): 1024 kilobytes
-
Gigabyte (GB): 1024 megabytes
-
Terabyte (TB): 1024 gigabytes
-
Petabyte (PB): 1024 terabytes
-
Exabyte (EB): 1024 petabytes
-
Zettabyte (ZB): 1024 exabytes
-
Yottabyte (YB): 1024 zettabytes
As data storage and processing capabilities continue to grow, we are increasingly encountering these larger units in everyday technology.
Practical Applications and Examples
Understanding data unit conversions is essential in various scenarios:
-
File Size Management: Knowing the size of files in different units helps in managing storage space and selecting appropriate storage media (e.g., USB drives, cloud storage).
-
Data Transfer: Understanding data transfer speeds (often expressed in Mbps or MBps) helps in estimating the time required to download or upload large files.
-
Network Capacity Planning: Network administrators need to accurately estimate network bandwidth to handle data traffic efficiently. Inaccurate conversions can lead to bottlenecks and performance issues.
-
Database Management: Database administrators need to understand data sizes to optimize database performance and storage capacity.
-
Software Development: Software developers must account for data sizes to create efficient and scalable applications.
Common Misconceptions and FAQs
Several misconceptions surround data unit conversions. Let's address some common questions:
Q1: Why is it 1024 and not 1000?
A1: This is due to the binary nature of computing. Computers operate using binary code (0s and 1s), and powers of 2 are inherently more efficient for computation. While 1000 is a convenient approximation, 1024 (2<sup>10</sup>) represents the actual number of bytes in a kilobyte, reflecting the underlying binary system.
Q2: My operating system shows a different file size than the calculation. Why?
A2: Operating systems often use different formatting techniques, leading to slightly varying representations of file sizes. Furthermore, some file systems might add overhead data, resulting in discrepancies between the calculated size and the reported size.
Q3: How do I convert other units like GB to TB?
A3: The principle remains the same. To convert gigabytes (GB) to terabytes (TB), you would divide the number of gigabytes by 1024 (or use the approximation of 1000). Similarly, you can convert between any pair of units in the hierarchy by using the appropriate conversion factor (powers of 1024).
Q4: What's the difference between MBps and Mbps?
A4: MBps (Megabytes per second) and Mbps (Megabits per second) represent data transfer speeds. One byte is equal to 8 bits, so 1 MBps is equal to 8 Mbps. This distinction is important when comparing data transfer rates advertised by internet providers or storage devices.
Conclusion: Mastering Data Unit Conversions
Converting 200,000 KB to MB is a fundamental skill in the digital world. While the basic calculation is simple, understanding the underlying principles and the significance of using the precise conversion factor (1024) is crucial for accurate data management and efficient utilization of resources. This knowledge is essential for anyone working with computers, data storage, networks, and related technologies. By grasping the relationships between different units of measurement and avoiding common misconceptions, we can ensure accuracy and efficiency in handling digital information. Remember that this understanding is not merely an academic exercise; it's a practical skill with far-reaching implications in our increasingly data-driven world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Milliliters In A Gallon
Sep 04, 2025
-
38mm Is How Many Inches
Sep 04, 2025
-
80cm In Feet And Inches
Sep 04, 2025
-
Cubic Inches To Liters Calculator
Sep 04, 2025
-
Millimeter To Square Feet Conversion
Sep 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 200 000 Kb To Mb . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.