100 Ppm In Mg Ml
thedopedimension
Aug 27, 2025 · 5 min read
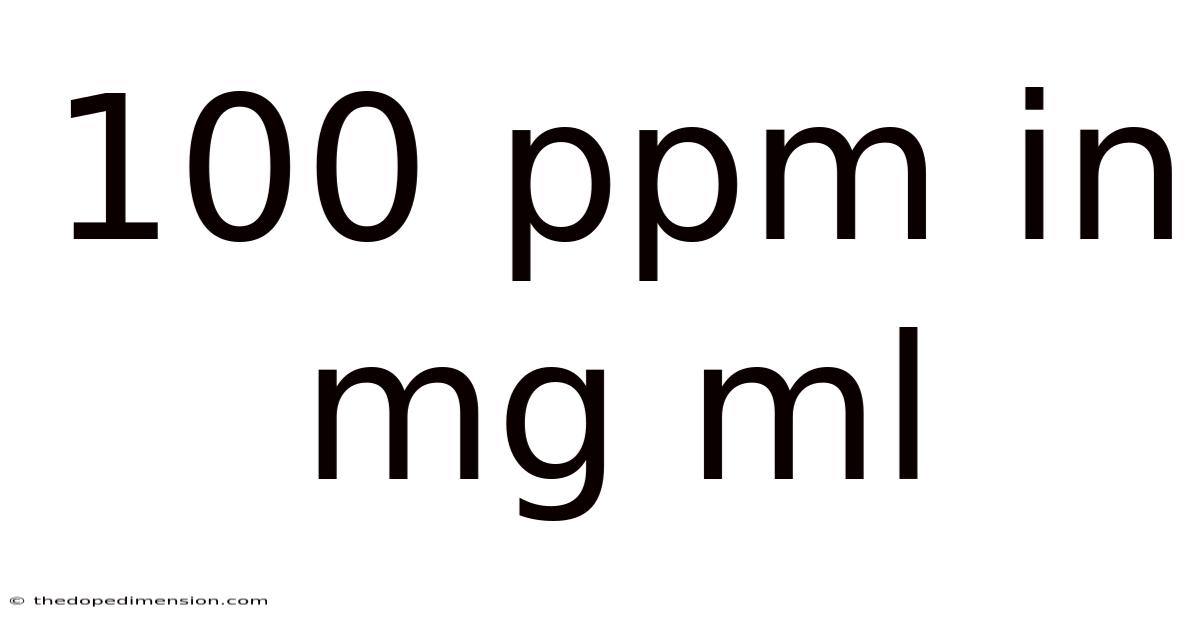
Table of Contents
Understanding 100 ppm in mg/mL: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction:
Many scientific and industrial applications require precise concentration measurements. Parts per million (ppm) is a common unit used to express very low concentrations, often for trace elements or contaminants. Understanding the conversion between ppm and mg/mL (milligrams per milliliter) is crucial for accurate calculations and experimental design. This article provides a comprehensive explanation of how 100 ppm translates to mg/mL, along with detailed examples and considerations for various applications. We'll delve into the underlying principles, address common misconceptions, and offer practical tips for handling such low concentrations.
What is ppm (Parts Per Million)?
Ppm represents the number of units of a substance per million units of the solution or mixture. It's a dimensionless unit, meaning it doesn't inherently have a unit like grams or liters attached. Think of it as a ratio: 1 ppm is equivalent to 1 unit in 1,000,000 units. This unit is incredibly useful for expressing extremely low concentrations where using percentages would result in cumbersome decimal values.
What is mg/mL (Milligrams per Milliliter)?
Mg/mL, on the other hand, is a unit of concentration expressing the mass (in milligrams) of a solute dissolved in a volume (in milliliters) of solvent. This is a measure of concentration directly related to mass and volume.
Converting ppm to mg/mL: The Key Relationship
The conversion between ppm and mg/mL depends critically on the density of the solution. For dilute aqueous solutions (solutions where water is the solvent), the density is approximately 1 g/mL (or 1 mg/µL). This simplification is often used because the density of dilute aqueous solutions is very close to the density of water (approximately 1 g/mL). Under this assumption, 1 ppm is approximately equal to 1 mg/L.
Therefore, to convert ppm to mg/mL, you need to consider the density and use the following formula (assuming density of 1 g/mL):
ppm = (mg solute / mL solution) * 1000
Solving for mg/mL:
mg/mL = ppm / 1000
100 ppm in mg/mL (using the approximation):
Applying the above formula for a solution with a density approximately equal to 1 g/mL:
mg/mL = 100 ppm / 1000 = 0.1 mg/mL
Therefore, under the assumption of a density of 1 g/mL, 100 ppm is approximately equal to 0.1 mg/mL.
Considering Density Variations: A More Accurate Approach
While the approximation of 1 g/mL is suitable for many dilute aqueous solutions, it's crucial to remember that it's not universally applicable. The density of a solution can vary depending on the solute, its concentration, and the temperature. For more accurate calculations, you must account for the actual density of the solution.
The general formula, accounting for density (ρ), is:
ppm = (mg solute / mL solution) * ρ * 1000
where:
- ppm = parts per million
- mg solute = mass of the solute in milligrams
- mL solution = volume of the solution in milliliters
- ρ = density of the solution in g/mL
To calculate mg/mL, rearrange the formula:
mg/mL = ppm / (ρ * 1000)
This formula allows for a more precise conversion, especially when working with solutions of higher solute concentration or non-aqueous solvents.
Example Calculations:
Let's illustrate with different scenarios:
Scenario 1: Dilute Aqueous Solution
A solution contains 100 ppm of NaCl in water. Assuming the density of the solution is approximately 1 g/mL:
mg/mL = 100 ppm / (1 g/mL * 1000) = 0.1 mg/mL
Scenario 2: Solution with Different Density
A solution contains 100 ppm of a solute in a solvent with a density of 1.2 g/mL:
mg/mL = 100 ppm / (1.2 g/mL * 1000) ≈ 0.083 mg/mL
As you can see, the density significantly impacts the mg/mL value. Ignoring density variations can lead to substantial errors in concentration calculations.
Practical Applications:
The conversion between ppm and mg/mL is crucial in numerous fields:
- Environmental monitoring: Determining the concentration of pollutants in water or air samples.
- Pharmaceutical industry: Precisely formulating drug solutions.
- Food science: Analyzing the presence of contaminants or additives in food products.
- Analytical chemistry: Preparing standard solutions for calibration curves.
- Materials science: Characterizing the composition of alloys or other materials.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
-
Q: Can I always assume a density of 1 g/mL for water-based solutions?
- A: For dilute solutions (low concentration of solute), the approximation is usually acceptable. However, for higher concentrations, it's essential to measure the actual density of the solution for accurate results.
-
Q: What if my solution isn't water-based?
- A: You absolutely cannot use the approximation. You must determine the density of your solution experimentally using a densitometer or pycnometer and apply the formula considering the actual density.
-
Q: How do I measure the density of my solution?
- A: Density can be measured using a variety of instruments, including:
- Hydrometer: A simple device that floats in the liquid, and the density can be read directly from the scale.
- Densitometer: Provides very precise density measurements using various principles, such as oscillating U-tube.
- Pycnometer: A precisely calibrated glass vessel used to determine the density by measuring the mass of a known volume of liquid.
- A: Density can be measured using a variety of instruments, including:
-
Q: What are the units for density?
- A: Density is typically expressed in g/mL (grams per milliliter) or g/cm³ (grams per cubic centimeter). These are equivalent units.
Conclusion:
Converting 100 ppm to mg/mL requires careful consideration of the solution's density. While the approximation of 0.1 mg/mL is valid for many dilute aqueous solutions, precise calculations require accounting for the actual density using the provided formula. Understanding this conversion is fundamental for various scientific and industrial applications demanding precise concentration measurements. Always remember to prioritize accurate density determination, especially when working with solutions of higher concentrations or non-aqueous solvents to ensure the reliability of your experimental results and avoid potential errors in interpretation.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Converter Chilean Pesos To Dollars
Aug 27, 2025
-
25 Acres To Sq Ft
Aug 27, 2025
-
Air Conditioning Btu To Tons
Aug 27, 2025
-
Cu In To Cu Yard
Aug 27, 2025
-
How Far Is 10 Kilometers
Aug 27, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 100 Ppm In Mg Ml . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.